For two mothers,
justice harder to reach amid pandemic

Two
mothers share how it feels to be prisoners of misery. On top of the
uncertainties brought by the Covid-19 pandemic, Marites Asis
agonizes over how the justice system has treated her daughter and
her late granddaughter, baby River, while Barbara Ruth Angeles has
to endure the loss of a daughter to sickness while seeking justice
for her son, who’s been in jail for months.
By
AIE BALAGTAS SEE
Philippine Center for Investigative Journalism
December 2, 2020
The wheels of justice are
grinding exceedingly slow for Marites Asis and Barbara Ruth Angeles.
Marites is the mother of
Reina Mae “Ina” Nasino, an urban poor leader who was arrested in
Manila in November 2019. Ina learned she was pregnant weeks before
her transfer to Manila City Jail and gave birth to baby River on
July 1, only to be separated from her newborn after a month.
Marites became worried not
only over Ina’s freedom and safety, but also over baby River’s
health. River, who was dependent on formula milk and donations from
the milk bank, was confined at the Philippine General Hospital after
contracting pneumonia in September. Baby River’s death sparked
public outrage as Ina was not allowed to visit the hospital and was
given only six hours to say goodbye to her baby.
Painter Barbara Ruth
Angeles has a similar story. It’s been months since she last saw her
son Inno, who was arrested on what she said were trumped-up drug
charges in Quezon City in 2018. To add to her misery, Inno’s older
and only sister died of bladder problems in August.
Inno was not able to say
goodbye.
Barbara Ruth has yet to
properly mourn the sudden passing of her eldest child as she is busy
earning a living while finding ways to free Inno. Barbara Ruth is
also busy taking care of her 12-year-old granddaughter, who is now
an orphan.
Marites and Barbara Ruth
are free but mired in misery that could only be cured by the
delivery of justice.
Here are their stories, in
their own words.

Justice is heavy handed for Reina Mae
Nasino and baby River
By
Marites Asis (as told to Aie
Balagtas See)
I found out that my
daughter Ina was pregnant the same time Covid-19 struck. I felt the
weight of heaven crash down on me.
I couldn’t give an
interview without crying. At night, I even cry myself to sleep.
You’d think I was crazy.
I learned about my
daughter’s pregnancy in February, a few weeks before the police were
set to transfer her to Manila City Jail.
That’s why when lockdowns
were imposed, I was anxious. You need social distancing, but they’re
cramped in a dormitory that houses 111 people.
It seemed risky for my
daughter to be pregnant and at the same time detained in jail, where
she could catch the virus.
I was asleep when Ina was
arrested [on Nov. 5, 2019]. Someone went to my house at about 5 a.m.
and told me about Ina’s arrest. The person said she was taken to the
CIDG (Criminal Investigation and Detection Group) office in Manila
Police District (MPD). In short, I rushed to MPD around 5 a.m.
I was hysterical.
I went to Ate Vicky, my
older sister, the woman who raised all of us, including Ina. We
consider her our mother.
Ate Vicky said we should
go to MPD. At MPD headquarters, however, they did not allow us to
see Ina immediately.
Investigators were asking
them if they really owned those guns.
I was furious.
The police planted
evidence against Ina. I know my daughter. They planted guns and
grenades. During the arrest, the cops covered their faces with
pillows. Who in his right mind would do that to our youth?
It hurts so much to see
your child in jail.
You couldn’t even go out
because of coronavirus. You’re stuck at home. Anxious and worried.
Before coronavirus hit, I
would visit her in jail every day. I never missed a visit until
visitation rights were cancelled last March.
With the lockdown in
place, I felt helpless.
I always wonder how my
daughter is doing. Is she eating well? Can she take a shower in
private or do they take showers in groups?
I pity my daughter.
Because of the virus, we
could not see each other, especially when she was still pregnant.
Covid-19 exacerbated my pain.
She said maybe I could see
her again in October.
It’s difficult. It’s
really, really difficult. I couldn’t sleep at night. I would always
think of her. She would talk to us through video calls, and we were
happy to see her tummy grow.
But I felt so guilty. I
couldn’t take care of my own daughter.
Ina was supposed to give
birth on July 10 but she gave birth nine days early, on July 1.
I didn't even see her at
the hospital.
I was asleep. A jail
personnel called me at midnight. She instructed me to go to Fabella
Hospital as Ina was about to give birth.
I rushed to Ate Vicky once
again. Together we went to Fabella, hoping we could be by my
daughter’s side on that important day.
When we got there, the
hospital administration said visitors were not allowed because of
their Covid-19 protocols.
Anyway, the hospital said
Ina had given birth.
Ate Vicky and I went back
to Fabella on July 3 to bring diapers and water for the baby.
The security guards said
my daughter was still there. They didn’t allow us to see her, so we
asked if they could hand the package over to Ina.
On our way home, about
noontime, Ate Vicky’s phone rang. It was Ina. She said the baby was
crying because she could not produce milk. The baby was hungry.
It baffled us because we
thought she was still in the hospital. Ina said they returned to
jail on July 2.
No one told us. We just
found out. That gave us another bout of sharp pain.
The security guards played us for fools!
We attended to Ina first. When we reached the city jail, we were
told the baby was already given formula milk.
Then we stormed Fabella Hospital to confront the guards. We demanded
that they return the diapers and water. Those belong to us.
They didn’t even want to return the water and diapers, so I
complained at the hospital’s information center.
I last saw Ina when she handed the baby to us on [Aug. 13].
We barely met her. We were not supposed to see Ina. I just asked the
warden if I could have a glimpse of my daughter.
How do I feel? I’m filled with pain. I can witness the suffering of
my child.
I felt that Ina and my granddaughter did not want to be separated
from each other.
How I feel about Ina is the same with how she feels about my
granddaughter.
I don’t know why they treated her that way. As a mother, I felt
hurt. I don’t know how to explain it. She is not convicted yet.
It was painful to watch them [policemen and jail guards] surround my
daughter. It’s okay if they made her wear PPE (personal protective
equipment) because she needed to go back to jail. But to handcuff
her? As if it’s not a wake.
I have yet to move on.
I skip social media posts that remind me of what happened because
they bring back memories of when she was handcuffed at the wake. She
was looking at her child. She was not able to come close to her
infant’s coffin.
Then there’s the memory of men with high-powered guns barging in to
inspect the room and the toilet because they were afraid of getting
outfoxed.
You see? They did not give us the chance to bond.
That day, I ran out of tears to cry. All I could do was call them
out.
I didn’t have any tears left to cry after seeing my daughter’s
situation.
It was difficult to cry because I was enraged. I asked them to leave
the room because we didn’t need guns there.
They didn’t have to guard the burial. There were so many of them
that they outnumbered the mourners.
I tried to appeal to their hearts. I told them we knew it was an
order and we couldn’t do anything. Just the same I hoped they
realized it was a burial and a mother would be separated from her
child.
I only wish they had thought of that.
During our last conversation at the cemetery, Ina told me: “Ma, it’s
okay to put the baby inside the niche.”
Ina held my hand twice: during the wake and during the burial.
She told me: “Ma, give me your hand.” She held it tight.
She was trying to tell me that I needed to be strong. I told her:
“Be strong, we will fight back.”
Postscript:
I’m okay. But it’s not easy to forget because the trauma is still
there. I can go to work now.
Ina said it’s not yet the end of everything.
I filed a legal complaint over what they did during the baby's wake
and burial. How will I attain justice if I don’t complain? This
should serve them a lesson because they must not treat other people
the way they treated us.
Baby River died of pneumonia on Oct. 9. The court gave Reina Mae a
couple of three-hour furloughs to bid her child goodbye. The first
was to visit the wake, the second was to bury her child.
Not even an inch of her skin was able to touch River’s coffin. She
was made to wear a full hazmat suit during the visits because of the
threat of Covid-19. She was in handcuffs most of the time and was
surrounded by heavily armed government forces.
Their family was never given a chance to grieve.

Legal shortcuts in the drug war: From
‘palit-ulo’ to ‘amin-laya’
By
Barbara Ruth Angeles (as told to
Aie Balagtas See)
My son Inno will enter
into a plea-bargain agreement. I don’t have any choice left. I have
to take him out of jail.
My son does not want it,
but I have no choice. How else are we going to set him free? That
was why we opted for “amin-laya” (plea bargain).
The advice came from
lawyers and BJMP (Bureau of Jail Management and Penology) personnel.
They said it’s his first offense anyway.
I’m worried for my son, of
course, as entering into a plea bargain means having a permanent
criminal record. It’s similar to being convicted already, although
he is innocent.
But my son’s case has been
pending in court for two years. Within that period we only had about
four hearings even if the court had released a monthly schedule.
Reset. Reset. Reset.
Since my son couldn’t
prove his innocence in court, I told him that once he’s free, it’s
up to him to prove to himself that he’s not what the government had
accused him of.
Besides, the cops offered
this solution to us before, and they promised us they wouldn’t
oppose it.
I can take better care of
my son if he’s with me. I can tell him, “Don’t go out, don’t go with
these people.”
I just want this problem
to end. We’re all suffering because of it.
Then, there’s the
pandemic. The BJMP does not tell us the exact number of inmates
infected with Covid-19. It’s difficult because it’s congested there.
Actually, I had to take
risks and buy my son a P15,000 kubol (hut) so he could have his own
space, and that’s just plywood about a quarter of a meter in size.
It is very expensive
inside city jails. You’re aware of this: If you are poor, you will
starve to death inside our jails.
Since visitation rights
are suspended, my son and I communicate with each other through
phone calls. Imagine this: to get in touch with me, he needs to buy
call cards worth P100 for P300. The BJMP asks you to buy the call
cards from them.
I won’t tell you the exact
amount that I spend on my son but his budget for a week is my budget
for two weeks.
I don’t know what else
could happen. That’s why I said, “Son, just plead guilty.”
My son was arrested on May
3 (2018). Arrests of drug suspects spiked during that period because
of the drug war “quota”. I learned about that so-called quota from
the BJMP personnel. They blamed it for their population boom.
Go back to the day Galas
police station was raided over an extortion case. That’s how we
learned Inno was there.
At first, we had no idea
that Inno had been arrested. We looked for him in barangay halls and
police stations. We reported him as missing because we couldn’t
reach his phone.
I kept crying.
My daughter and I searched
everywhere. I thought he was killed because deaths related to bike
theft were rampant those days, so we scoured hospitals and funeral
parlors.
I posted about our search
for Inno on Facebook. One of my school batchmates advised me to
report it to 8888. I reported it to the Duterte hotline 8888 but it
was not able to help us.
On May 4, Galas Police
Station was raided over an extortion case involving its
anti-narcotics team.
A police investigator called me and said: “Go to Galas Police
Station immediately. Your son is here. Bring food and clothes.”
I was shocked. How did he
end up there?
No one entertained me at
the police station until I lost my cool.
Someone from GMA News told
me to get a good lawyer.
At that time, hiring a
private lawyer cost P300,000. Our case got delayed because we
couldn’t find one. Some were too old. His grandmother found someone
but I think he’s from Aklan.
We couldn’t grasp what was
happening. We were desperate to find a lawyer. It was mental
torture. We weren’t used to this. It was the first time someone in
the family got involved in a court case.
The most enraging part was
my son didn’t violate any law.
You know, initially, the
police didn’t even have a record of his arrest.
I talked to detainees and
some policemen at Galas. I learned that the SAID (Station
Anti-Illegal Drugs Division) cops were supposed to kill Inno as a
replacement for big fish that they’re extorting money from.
The policemen in Galas
said my son was intended for “palit-ulo.” (Palit-ulo, which
literally means head-swapping, is a scheme in which a drug suspect
gets freedom in exchange for ratting out on his or her suppliers.)
They said it was for a
“zero-zero.” You know zero-zero?
That meant they would kill
him.
The policemen tortured my
son.
I have evidence, including
the medico-legal report, and X-ray and CT scan results.
At the hospital, the
doctor said he had fractured ribs. They also saw a “metallic
forensic” in his left leg.
The doctor did not want
him to leave, but Galas police did not allow him to be operated on.
Despite his fractures and injuries, Galas turned him over to the
city jail.
We lost the chance to have
him treated. His wounds eventually healed in jail.
You asked how I’m doing?
It’s the first time
someone asked me that question.
Well, I’m not… I’m not
okay. I try to do my normal routine but emotionally, no, I’m not
okay. My daughter died in August while my son is in jail. She’s my
eldest and the only one I could rely on to deal with this problem.
We were able to get hold
of the CCTV [showing Inno’s illegal arrest] because of her.
I still couldn’t accept
that my daughter had passed away.
Inno was not able to say
goodbye. They had not seen each other for two years.
She was sick but was not
confined. Her resistance was down and I was afraid that she might
catch the virus in the hospital.
My daughter left behind
three children. The eldest child, an 11-year-old girl, does not have
a father. I’m taking care of her.
My granddaughter is
already worried that her life will fall apart if something happens
to me. I told her, nothing’s going to happen to me because I still
have a purpose in life.
I have faith in the Lord.
I never questioned God for
everything that I’m going through. I know he will not give me these
trials if I cannot overcome them.
I’m trying to be strong
for my son and for my granddaughter. If I falter, who would be
strong for them.
But it’s difficult.
Postscript:
I think my daughter is
guiding me. I feel better now. I started painting again 40 days
after her death.
I used to paint with dark
colors, colors that you can associate with death. This time, I’m
using positive and vibrant colors. My artwork seems alive.
Do I have peace of mind?
No. I can only have peace
of mind when my son is finally with me. -- PCIJ, December 2020
Aie
Balagtas See is a freelance journalist working on human rights
issues. Follow her on Twitter (@AieBalagtasSee) or email her at
aie.bsee@gmail.com for comments.
Inspired by The Marshall Project's Life Inside, Marites' and
Barbara's stories are part of PCIJ’s series on the criminal justice
system, which includes first-person accounts from current and former
detainees and their family members.

A
Dumagat woman breastfeeds her six-month-old baby while
waiting for their sitio’s turn to line up for relief
goods. |
Promotion,
protection of breastfeeding practices reap rewards
By
ANGELICA CARBALLO PAGO
Philippine Center for Investigative Journalism
October 21, 2020
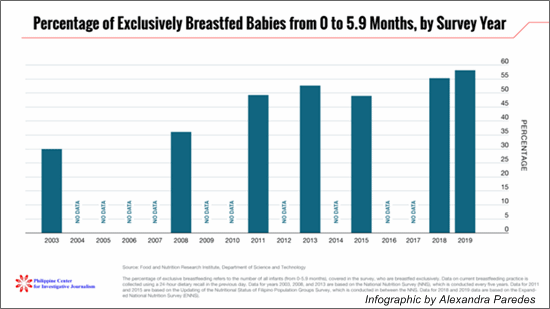
Exclusive breastfeeding among infants 0 to 5.9 months has nearly
doubled, from 30 percent in 2003 to 58 percent in 2019.
Women should still
breastfeed despite the pandemic, even those found to be positive for
Covid-19, according to a Department of Health (DOH) memorandum. This
shows how the government has been relentless in promoting
breastfeeding in the face of a formidable opponent – milk
manufacturing giants who have made their way into the consciousness
of Filipino mothers through massive advertising.
Despite the passage of the Milk Code 33 years ago, myths and
unfounded beliefs persist amid aggressive promotions by milk
manufacturers that claim to give a child advantage in terms of
health and IQ points.
Only 35.1 percent of babies are exclusively breastfed until 5 months
of age, according to the 2019 Expanded National Nutrition Survey of
the Department of Science and Technology – Food and Nutrition
Research Institute (DOST-FNRI), although exclusive breastfeeding
percentages have been increasing since 2003, but took a dip in 2015.
Nathalie Verceles, director of the University of the Philippines
Center for Women’s and Gender Studies, said the Milk Code was meant
to protect the interest of mothers and babies from aggressive
marketing strategies of formula milk companies. (See related story:
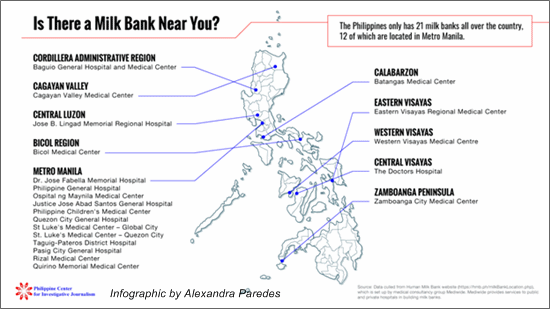
Milk and the pandemic: Milk Code confusion cripples LGUs response
for infants)
Mothers need support, according to Save the Children Philippines
health and nutrition adviser Dr. Amado Parawan. A mother’s decision
to breastfeed, he said, predates the birth of the child and will
depend on what she believes – or is made to believe. This decision
can also be affected by the support she gets – or doesn’t get – from
home, work and community.
|

Maryjoy
Mota shows the bottle used to feed baby Pia, when her family was
able to scrape a few hundred pesos to buy formula milk. |
Here’s a timeline of breastfeeding policies and how they have
influenced breastfeeding rates.
May 1981 – The International Code on Marketing of Breastmilk
Substitutes is adopted by the World Health Assembly. The aim is to
protect and promote breastfeeding by ensuring appropriate marketing
and distribution of breastmilk substitutes.
20 October 1986 – President Corazon Aquino signs Executive Order 51
or the Milk Code with its Implementing Rules and Regulations (IRR).
The Code regulates advertising of breastmilk substitutes, including
infant formula, other milk products, foods and beverages, feeding
bottles and teats.
1990 – Guided by the World Health Assembly resolutions, which state
that “follow-on or follow-up formulas are unnecessary because after
six months the baby starts to take complementary foods together with
sustained breastfeeding,” improvements were introduced on the IRR,
such as the ban on follow-on formulas. This was prompted by the 1987
Wyeth's invention of follow-on milk for children aged six months and
above that undermined the importance of breastfeeding. When the Milk
Code was being drafted, follow-on milk was not yet invented.
“Complementary food” includes food that is part of the local
culture.
2 June 1992 – The Rooming-In and Breast-Feeding Act, Republic Act
(RA) 7600, is passed, provides legal basis for rooming-in as a
national policy to encourage, protect and support breastfeeding.
2003 – The exclusive breastfeeding percentage among infants 0-5.9
months stands at 29.7 percent.
2004 – The Task Force Milk Code begins discussion and debate on the
first draft of the revised IRR of the Milk Code. Among those
consulted was Swiss multinational Nestlé, who represented formula
milk companies.
23 May 2005 – DOH Administrative Order (AO) 2006-0014 or the
National Policies on Infant and Young Children is issued. It states
that in times of crisis, breastfeeding is the first and best feeding
option for infants and young children. It requires mothers and
babies to remain together after delivery. Support must be given for
mothers to breastfeed even in crisis or emergencies.
2006 – The Pharmaceutical Healthcare Association of the Philippines
(PHAP) seeks a temporary restraining order on the revised IRR’s
implementation. After initially denying PHAP’s petition, the court
overturns its decision and issues a TRO on the revised IRR.
28 May 2007 – DOH AO 2007-0017 or the “Guidelines on the Acceptance
and Processing of Foreign and Local Donations during Emergency and
Disaster Situations,” states that “Infant formula, breastmilk
substitutes, feeding bottles, artificial nipples and teats shall not
be items for donation. No acceptance of donation shall be issued for
any of the enumerated items.”
09 October 2007 – The revised IRR of the Milk Code takes effect
after the Supreme Court partially upholds its validity. It strikes
down certain provisions, such as the prohibition on advertising and
promotion of breastmilk substitutes and introduces sanctions not
found in the law.
01 April 2008 – The Department of the Interior and Local Government
releases AO 2008-0055, or the “Guidelines on the acceptance and
processing of foreign and local donations during emergency and
disaster situations.” It endorses DOH AO 2007-0017 to all local
government units.
2008 – The exclusive breastfeeding percentage among infants 0-5.9
months rises to 35.9 percent.
16 March 2009 – RA 10028 or the Expanded Breastfeeding Act, which
amends RA 7600, is signed by President Gloria Macapagal Arroyo. It
establishes standards for workplaces, health facilities (with the
establishment of milk banks) and public places, and calls for
breastfeeding breaks and designated facilities in the workplace.
2011 – The exclusive
breastfeeding percentage among infants 0-5.9 months rises anew, to
48.9 percent.
21 December 2012 – RA
10354 or The Responsible Parenthood and Reproductive Health Act of
2012 is signed by President Benigno Aquino III. It includes
breastfeeding as an element of reproductive health care and provides
a basis for breastfeeding promotion and education.
2013 – More than half, or
52.3 percent, of infants 0-5.9 months are exclusively breastfed.
2015 – The exclusive
breastfeeding percentage among infants 0-5.9 months dips for the
first time to 48.8 percent.
29 November 2018 – RA
11148 or the “Kalusugan at Nutrisyon ng Mag-Nanay Act” is signed by
President Rodrigo Duterte. The law seeks to address the malnutrition
of infants and young and lactating women.
2018 – The exclusive
breastfeeding percentage among infants 0-5.9 months recovers
slightly to 54.9 percent.
17 April 2019 – RA 11311
or “An Act to Improve Land Transportation Terminals, Stations,
Stops, Rest Areas and Roll-On/Roll-Off Terminals, Appropriating
Funds Therefor and for Other Purposes,” establishes lactation
stations in transport terminals, stations, stops and rest areas.
2019 – Exclusive
breastfeeding improves to 57.9 percent.
11 May 2020 – DOH
Memorandum No. 2020-0237 or the “Interim Guidelines for the Delivery
of Nutrition Services in the Context of COVID-19 Pandemic” states
that mothers who are asymptomatic, or those with close contacts,
suspect, probable, or confirmed case of COVID-19 who do not have
severe illness and/or who are not in respiratory distress, can
continue breastfeeding, provided that they observe strict infection
control measures.
15 May 2020 – DOH
Memorandum No. 2020-0231 or the “Guidelines on the Standardized
Regulation of Donations, Related to EO 51,” provides guidelines on
how LGUs can help provide nutrition for non-breastfeeding children
under 3 years old. While donations are banned as stipulated in
various laws and orders, LGUs can procure formula milk and give them
to identified families. The memorandum still upholds the promotion
and protection of breastfeeding for infants and young children.
Sources:
Food and Nutrition Research Institute for breastfeeding data
Babymilkaction.org for Milk Code RIRR timeline
◄◄home
I
next►►