More than 94% of
global population experienced decline in freedom from 2019 to 2020
Press Release
January 26, 2023
TORONTO (GLOBE
NEWSWIRE) – While global freedom was already waning before COVID,
the response from governments during the pandemic accelerated the
loss of freedom worldwide, finds a new study released today by
Canada’s Fraser Institute and the U.S.-based Cato Institute.
“During the pandemic,
governments worldwide restricted freedom of movement, expression,
assembly and other freedoms even more than in previous years,” said
Fred McMahon, resident fellow at the Fraser Institute and co-author
of this year’s Human Freedom Index.
While we take no position
on the necessity of COVID policies, they unquestionably limited
freedom. From 2019 to 2020 (the latest year of available data), 94.3
per cent of the world’s population experienced a decline in freedom.
But again, freedom was on
the decline before COVID – the government response simply
accelerated the decline. Between 2007 (the highpoint for human
freedom) and 2019, freedom declined for 79 per cent of the world’s
population.
The index measures
personal freedom – the rule of law, safety and security, identity
and relationships (i.e. the freedom to choose your relationship
partner), freedom of movement, speech, assembly and religion –
alongside economic freedom, the ability of individuals to make their
own economic decisions.
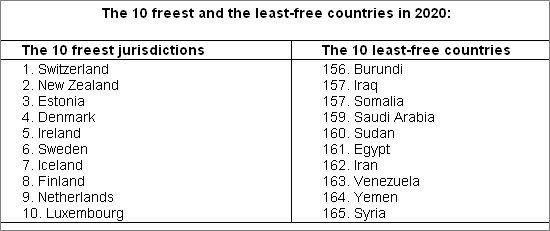
Switzerland, once again,
tops this year’s freedom ranking followed by New Zealand, Estonia,
Denmark, Ireland, Sweden, Iceland, Finland, the Netherlands and
Luxembourg. The five least-free countries are (in descending order)
Egypt, Iran, Venezuela, Yemen and Syria.
Overall worldwide rankings
for other significant countries include Japan (16), Germany (18),
the United Kingdom (20), the United States (23), South Korea (30),
France (42), Argentina (74), South Africa (77), Brazil (80), India
(112), Russia (119), Nigeria (124) and China (152).
Regionally, Western
Europe, North America (Canada and the United States) and Oceania
have the highest levels of freedom while the Middle East and North
Africa, sub-Saharan Africa and South Asia have the lowest levels.
Crucially, people in freer
countries are more prosperous than those in less-free countries. For
example, the average per-capita income for the top-quartile
countries on the index was US$48,644 compared to US$11,566 for the
least-free quartile in 2020.
“When government limits
the ability of people to move, assemble and speak freely, people are
less able to the lives they want to live,” said Ian Vásquez, report
co-author and director of the Cato Institute’s Center for Global
Liberty and Prosperity.
The complete index, a
joint project of the Fraser Institute and the Cato Institute, is
available as a free PDF download at www.fraserinstitute.org. The
co-authors of the report are Ian Vasquez, Vice President,
International Studies, Cato Institute, Ryan Murphy, associate
professor, Bridwell Institute for Economic Freedom, Southern
Methodist University, and Guillermina Sutter Schneider, data
scientist and research manager, Center for Global Liberty and
Prosperity, Cato Institute.